The Virtual Brain Train – Now Boarding
The Virtual Brain Train – Now Boarding
When
Bookings
Event Type
If you register for this event during the live period, you will get access to all recordings!
Discover The Fundamental Language of The Brain – Neurotransmitters for Behavior Nerds
Your Experts
PhD Simon Gadbois, Dr. Robert Falconer-Taylor, Dr. Laura Donaldson, Dr. Eduardo Fernandez, Dr. Karolina Westlund,
PhD, CAAB Kristyn Vitale, Daniel Shaw, Dr. Kristina Spaulding.
CEUS Continued Education Units –
Pet Professional Accreditation Board – 15, CCPDT – 5 CEUs for Trainers and 10 CEUs for Behavior Consultants. Pat Miller Academy 12, KPA 15. IAABC 15
Neurotransmitters are essential to learning and behavior because they serve as the chemical messengers that allow neurons (nerve cells) to communicate with one another throughout the brain and body. This communication forms the basis of all brain functions, from basic physiological processes to complex cognitive abilities and emotional responses.
Register Today – Set up a subscription and pay over five months, or scroll down and register and pay now.
- Choose your payment plan: PPG Members or General Public
- Set up your subscription (PPG Members $130.00, Public $180.00)
- Receive your subscription confirmation email with your event code
- Use your event code to register for the event for FREE, having signed up for the payment plan
- Receive your event confirmation email and Zoom links.
Your ticket provides access to all live sessions across the five days, as well as 12 months of access to the recording stage.
Why are neurotransmitters so crucial, and why do I need to understand more about them?
Neurotransmitters are crucial because
- Information Transmission: Neurotransmitters transmit signals across the tiny gaps (synapses) between neurons. Without them, electrical impulses in one neuron couldn’t effectively influence the next, and the entire nervous system would cease to function.
- Regulation, Mood, Emotion, and Motivation: Different neurotransmitters are associated with specific psychological functions.
- Dopamine is often linked to pleasure, reward, and motivation. It plays a significant role in learning by reinforcing behaviors that lead to positive outcomes. It’s also involved in attention and focus.
- Serotonin plays a significant role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and impulse control. Imbalances in serotonin are linked to conditions like depression and anxiety, which profoundly impact behavior.
- Norepinephrine (also known as noradrenaline) is associated with arousal, attention, and the “fight-or-flight” response, all of which are crucial for how we respond to our environment.
- Endorphins are the body’s natural pain relievers, contributing to feelings of euphoria and influencing our perception of pain and overall well-being.
- Memory and Learning.
- Acetylcholine plays a vital role in memory, learning, motivation, and attention. It’s heavily involved in the formation of new memories and is implicated in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease when its levels are low.
- Glutamate is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain, playing a crucial role in synaptic plasticity —the process by which synapses strengthen or weaken over time. This plasticity is the fundamental cellular mechanism underlying the formation of learning and memory (e.g., long-term potentiation).
- GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) is the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter, helping to calm neural activity. A proper balance between excitatory (like glutamate) and inhibitory (like GABA) signals is essential for optimal brain function, including learning.
- Shaping Behavior and Responses: By influencing the activity of different brain circuits, neurotransmitters dictate how we perceive, interpret, and respond to stimuli. They contribute to our decision-making, motor control, and even our ability to adapt to new situations. For example, the interplay of dopamine and acetylcholine is constantly at work, creating “ebb and flow” cycles that prepare the brain for continuous learning, even in the absence of immediate external rewards.
- Clinical Significance: Dysregulation in neurotransmitter systems is implicated in a wide range of neurological and psychiatric disorders, including depression and anxiety disorders. Understanding the role of neurotransmitters helps us comprehend and target imbalances, thereby alleviating symptoms and enhancing function.
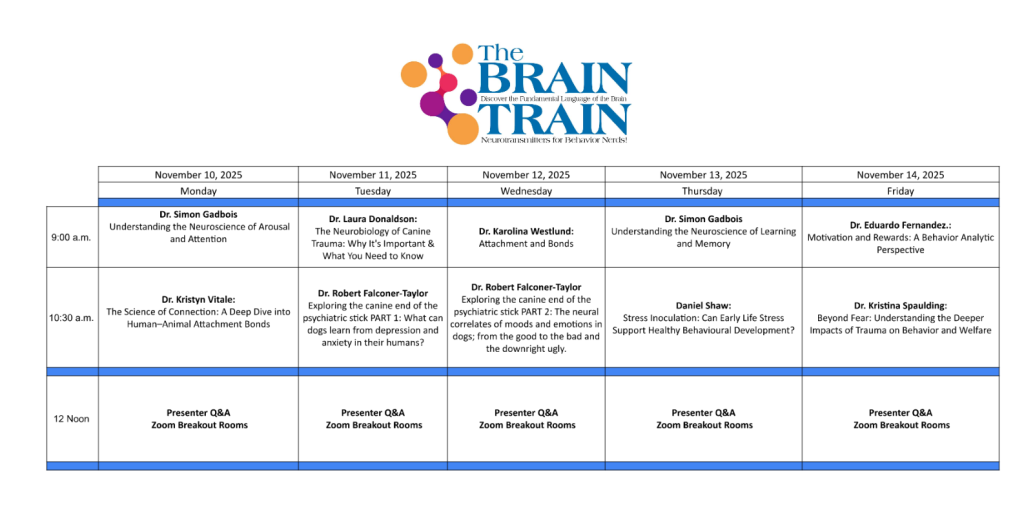
Grab Your Event Session Guide Here
The Event Schedule
Bookings
Bookings are closed for this event.